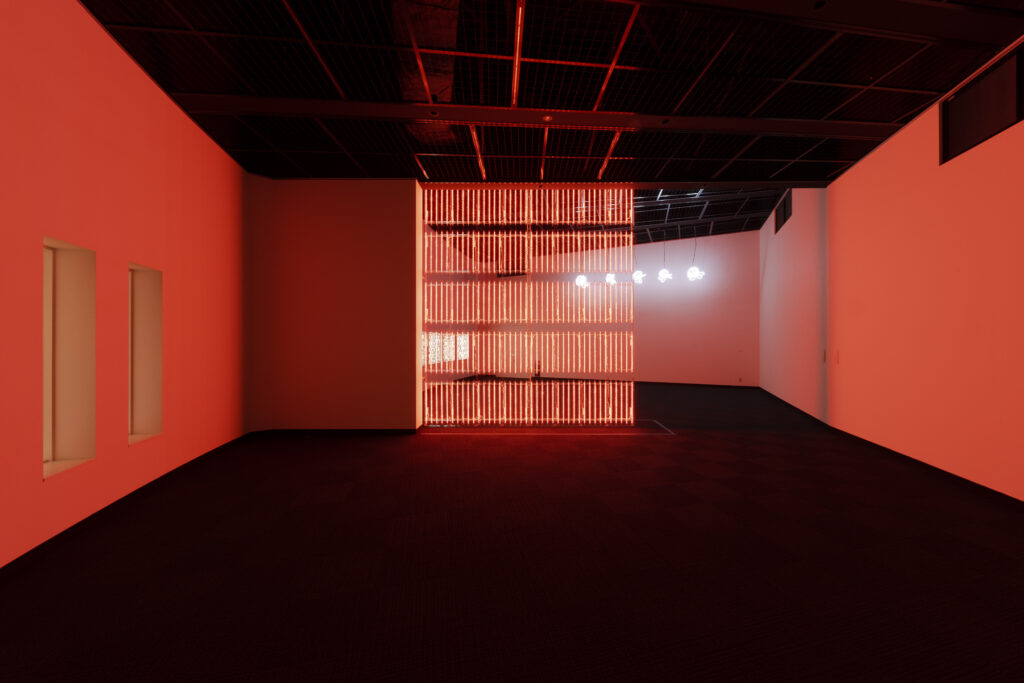
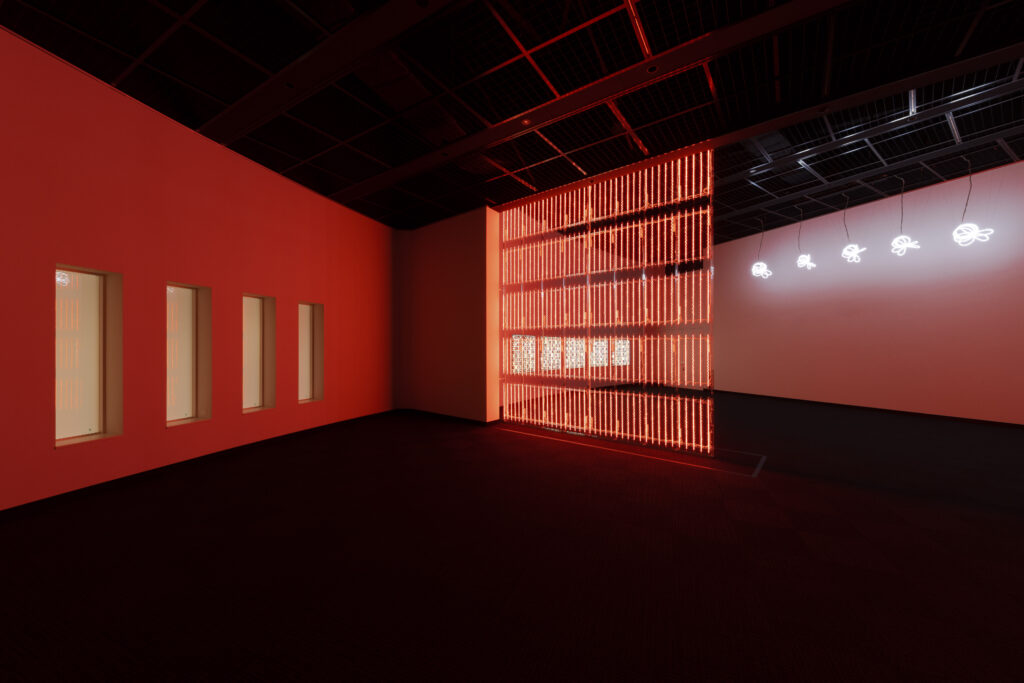
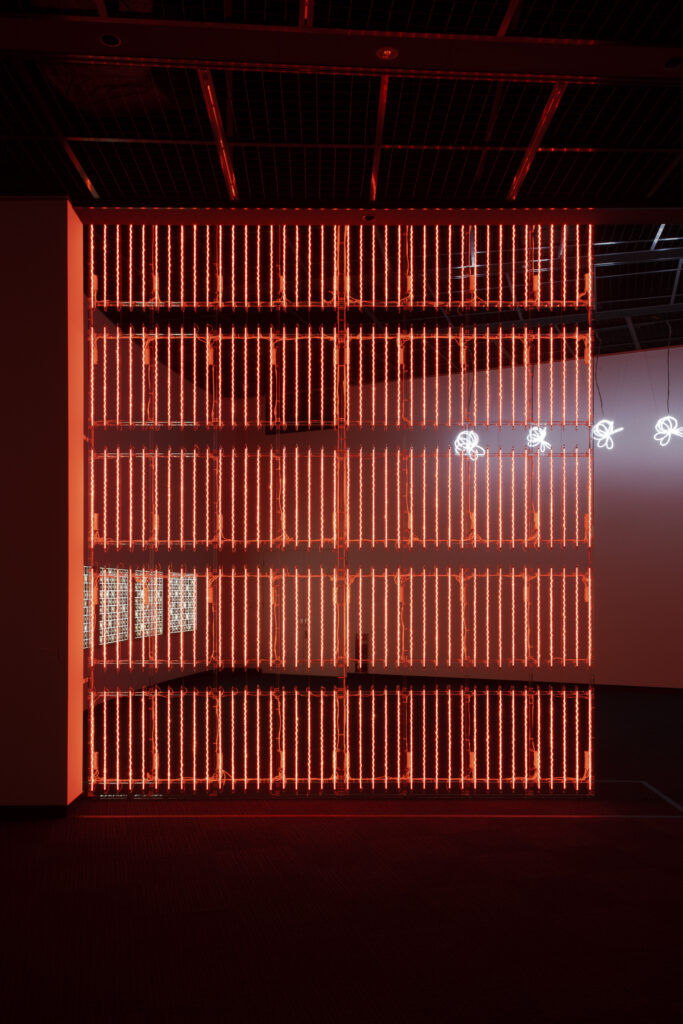
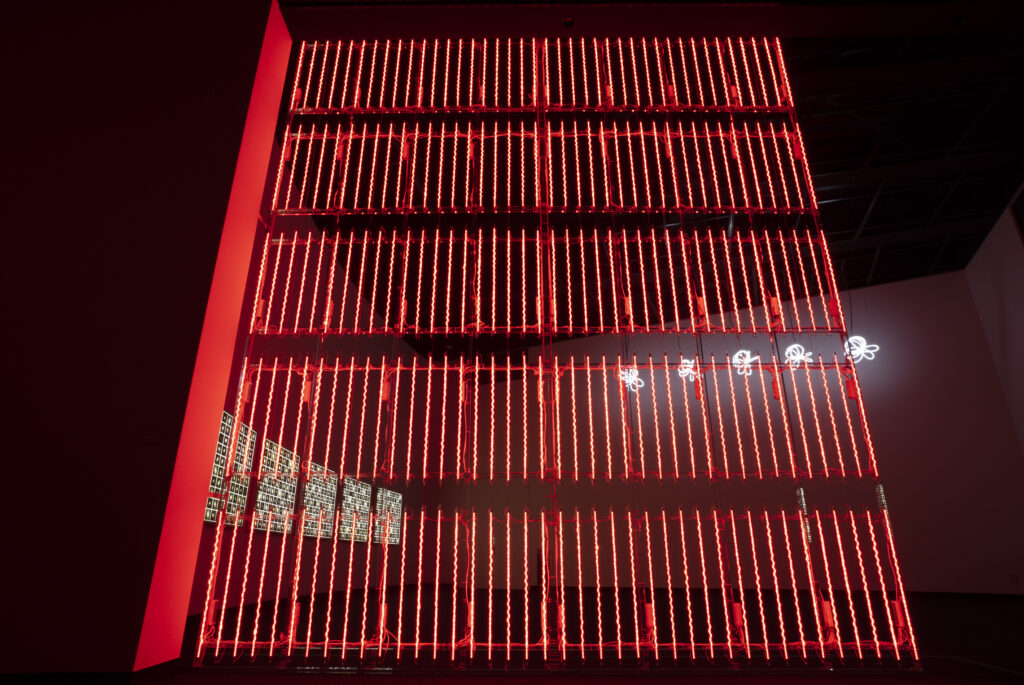
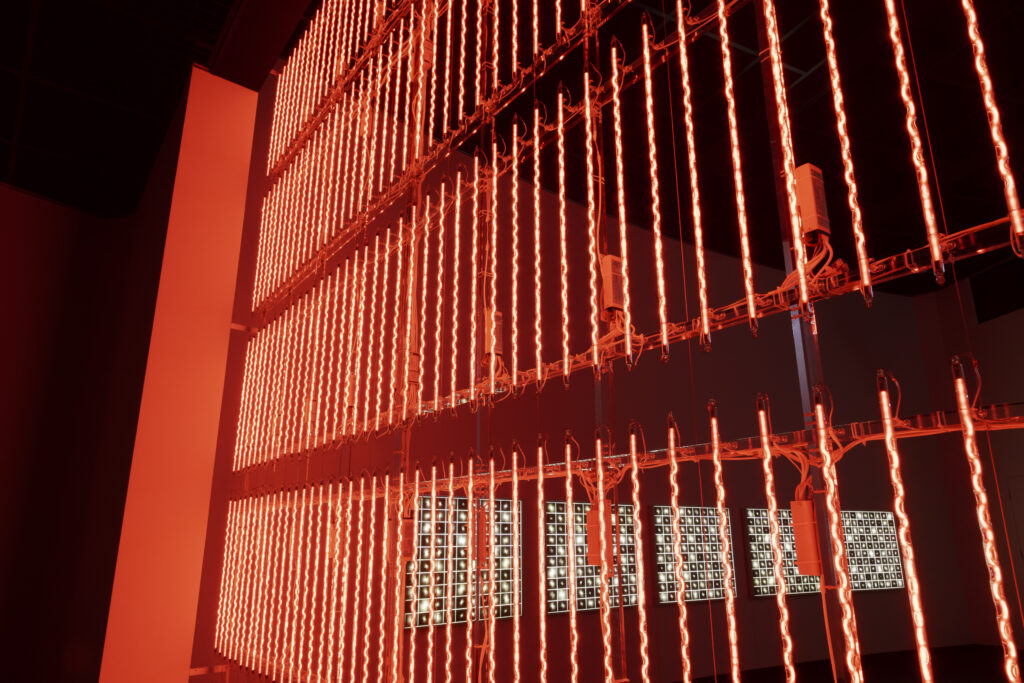
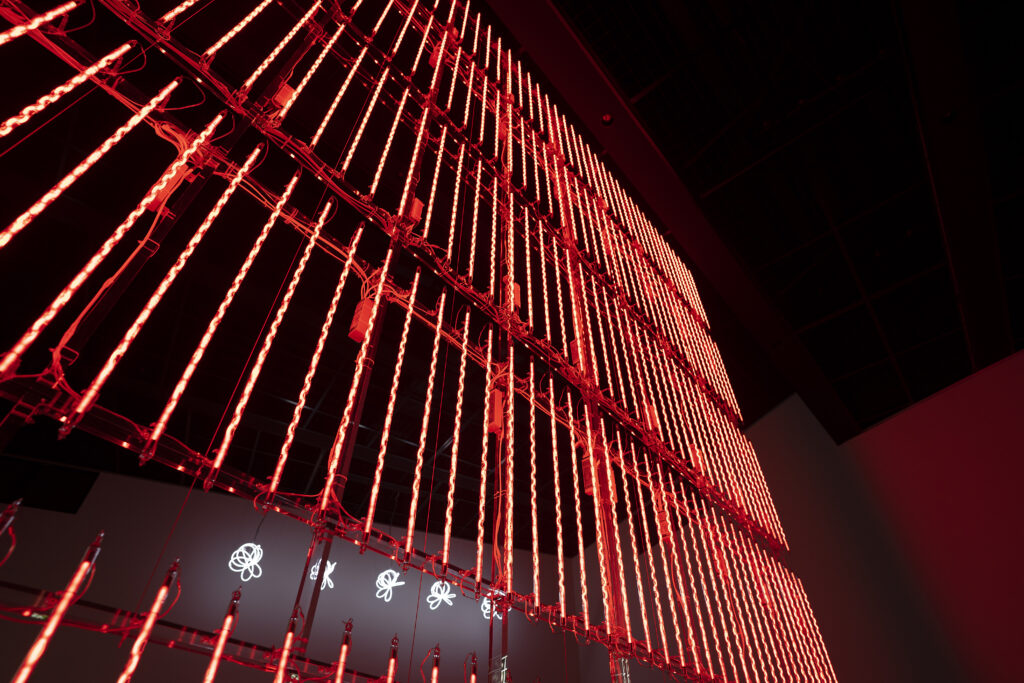
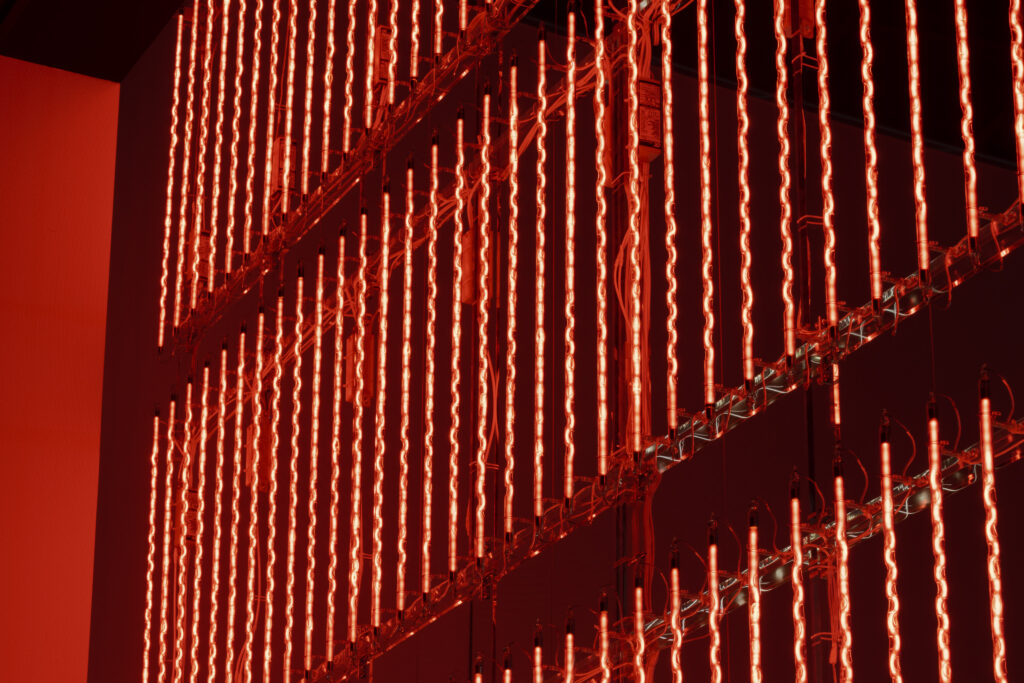
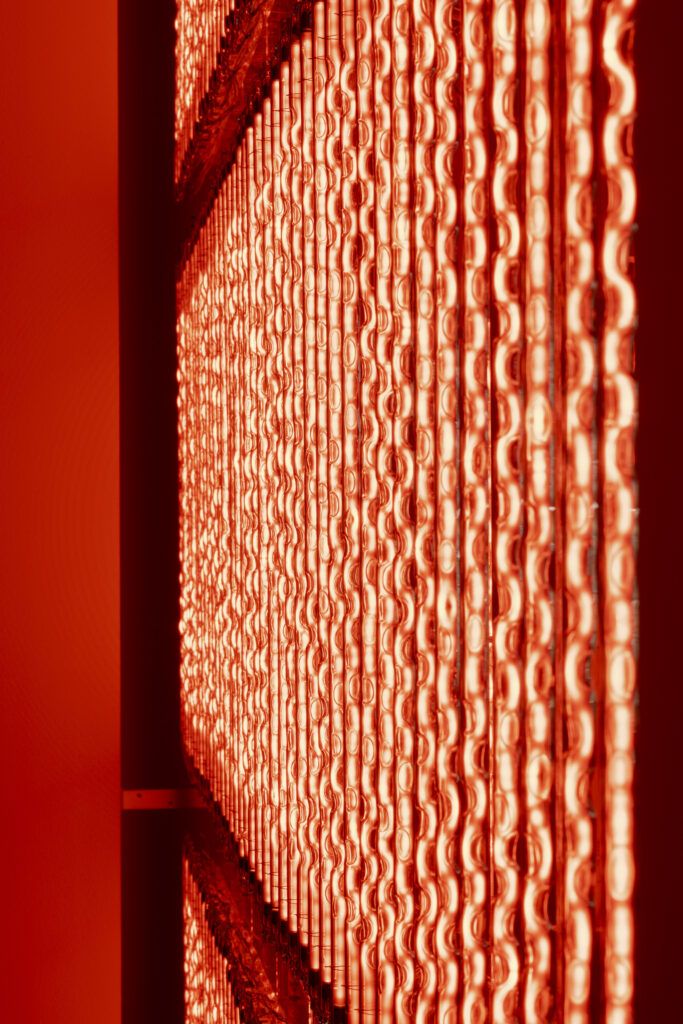
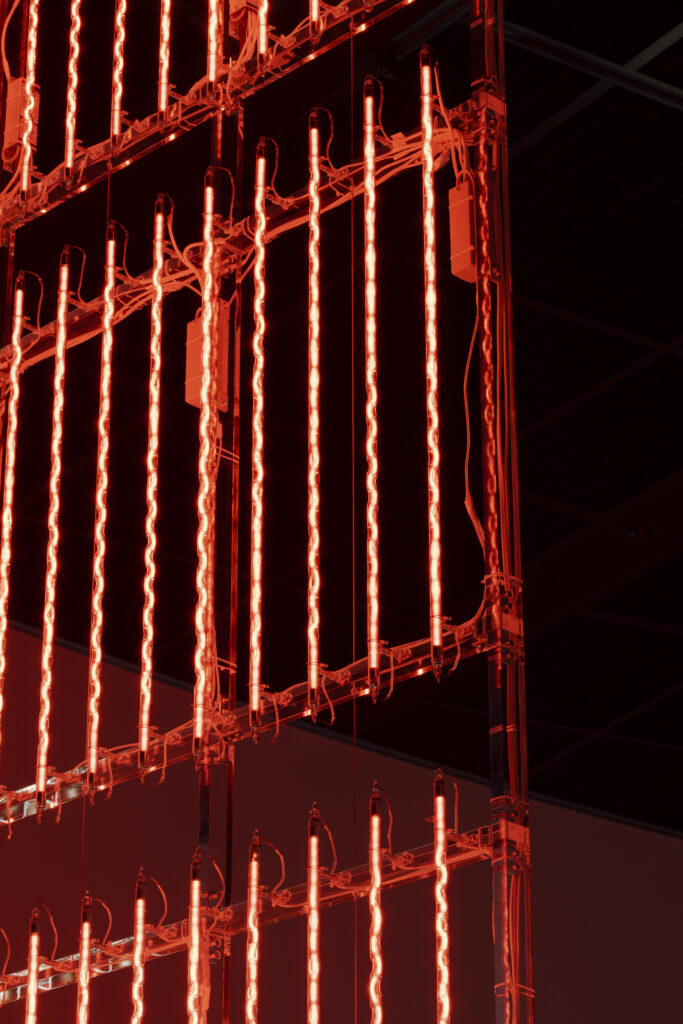
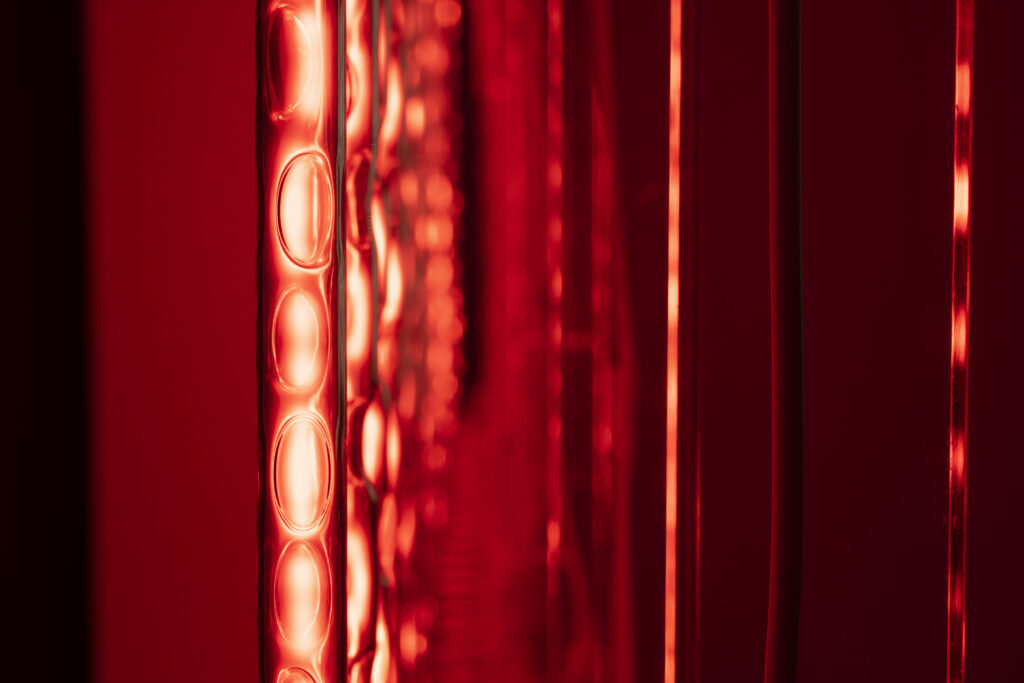
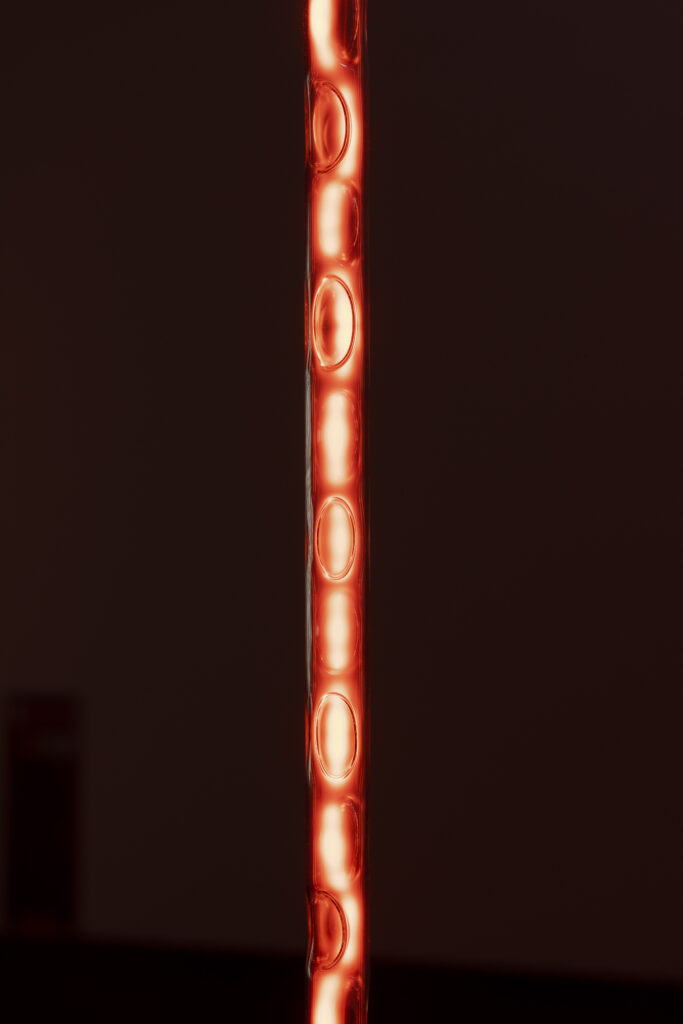
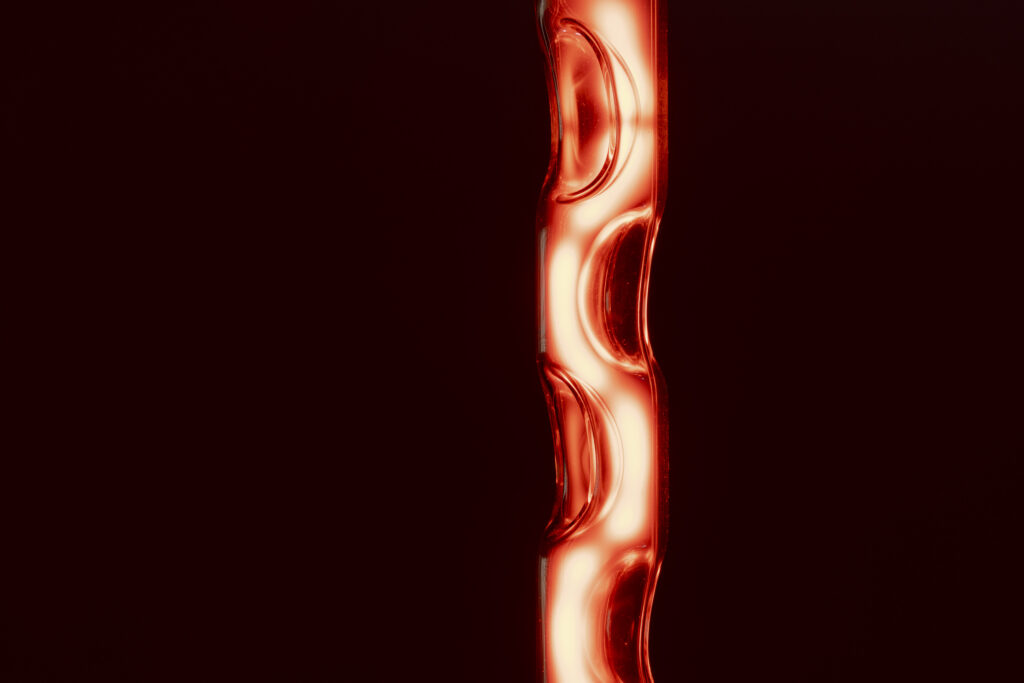
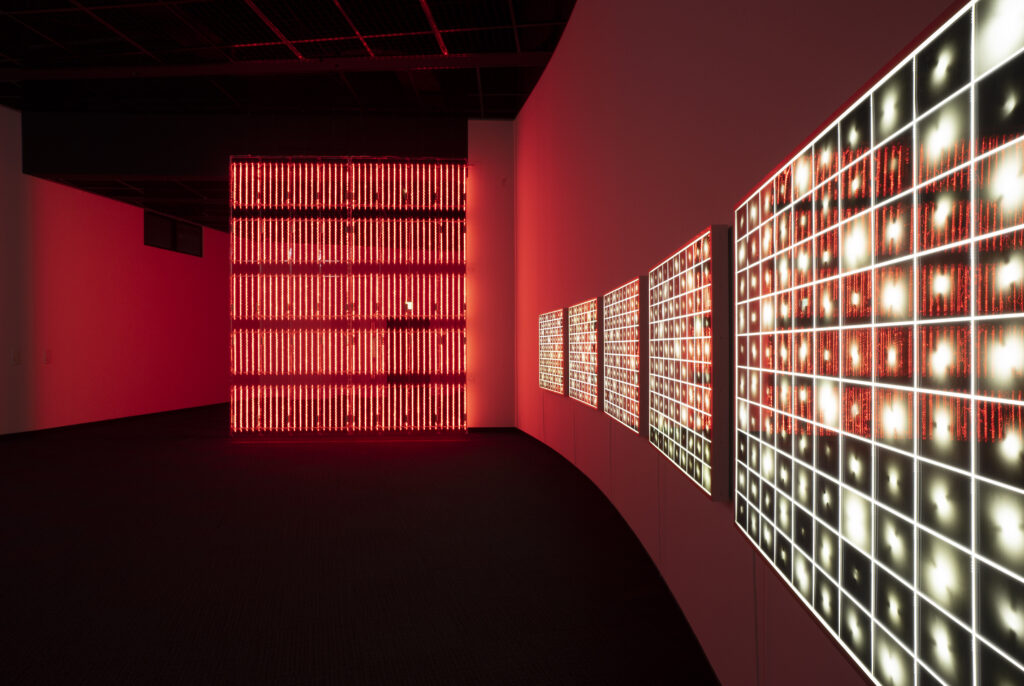
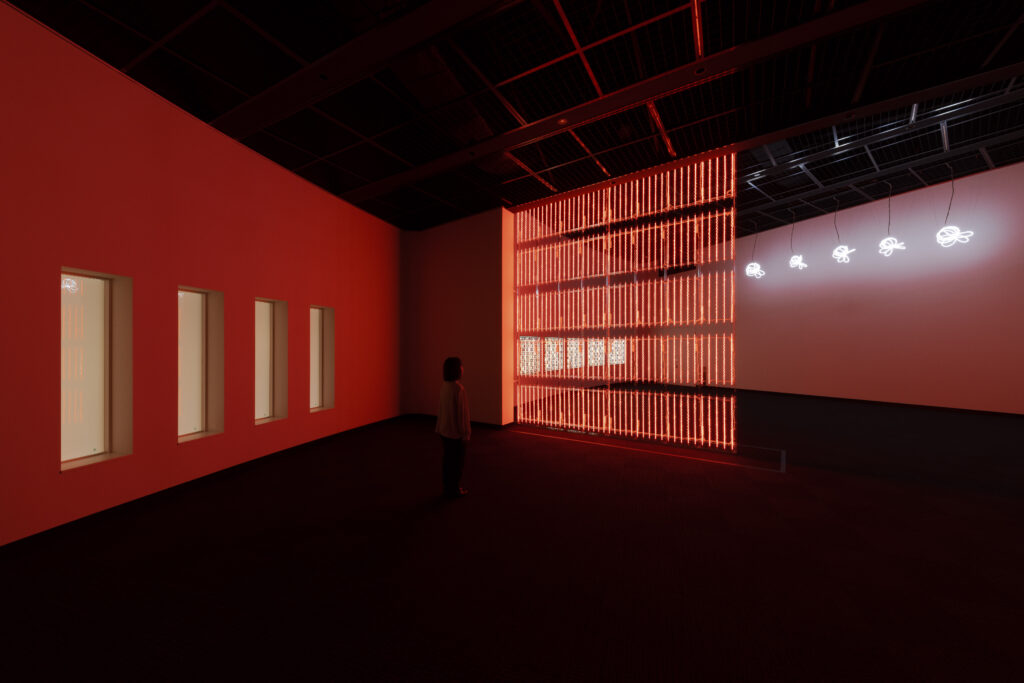
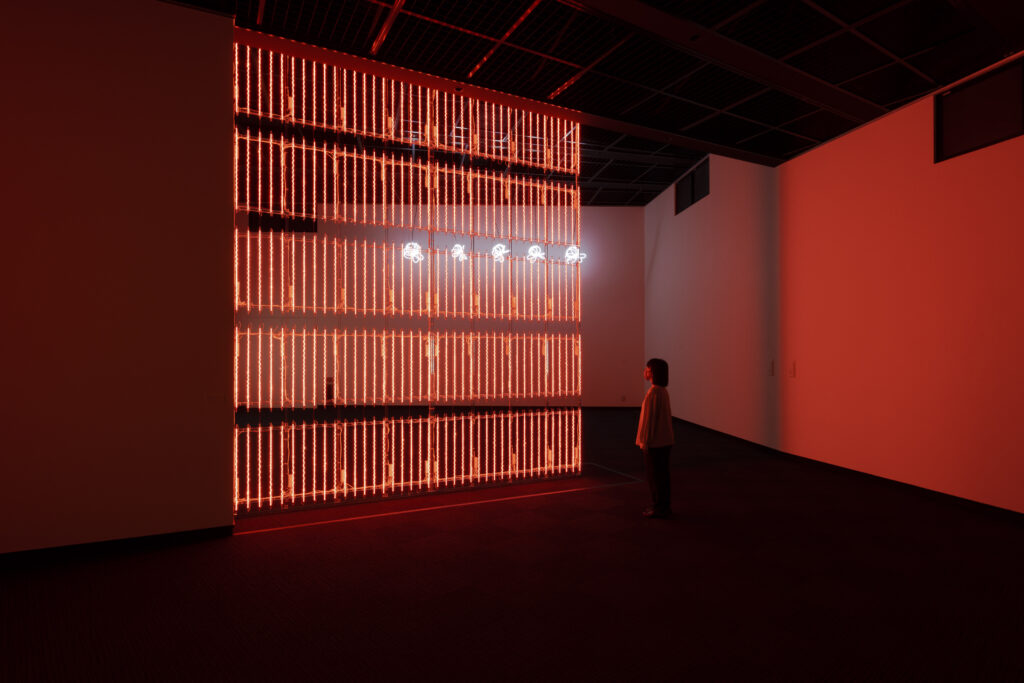
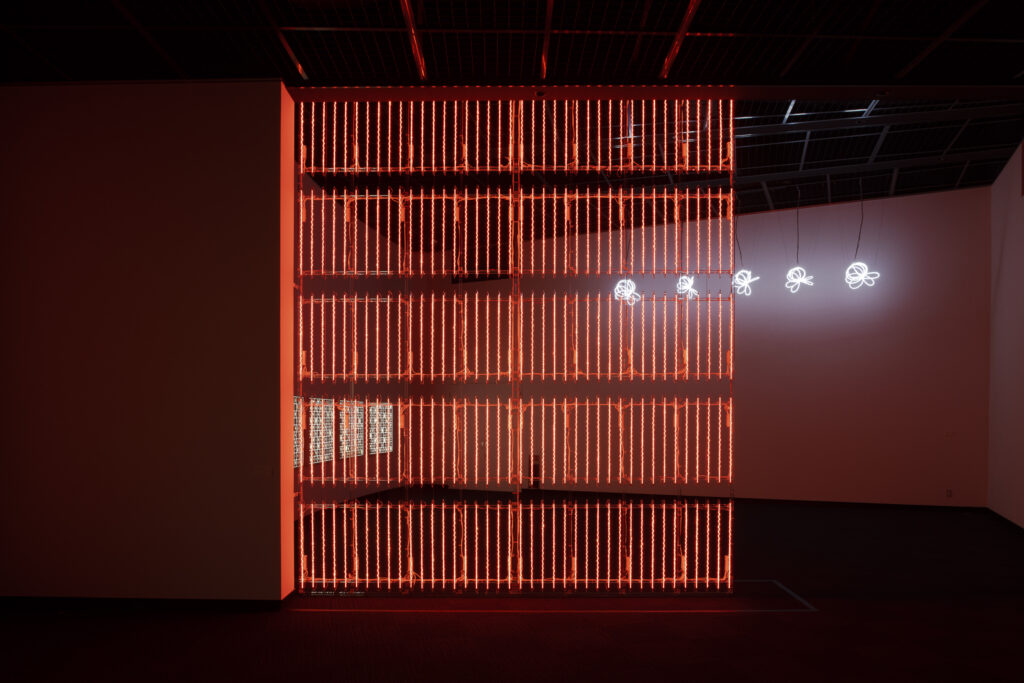
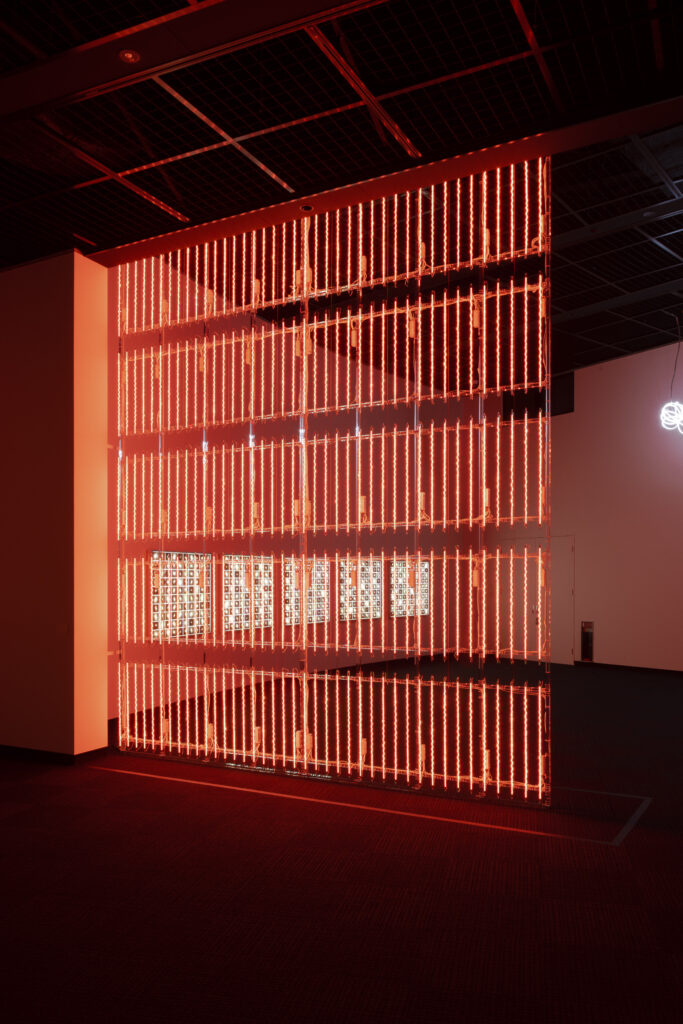
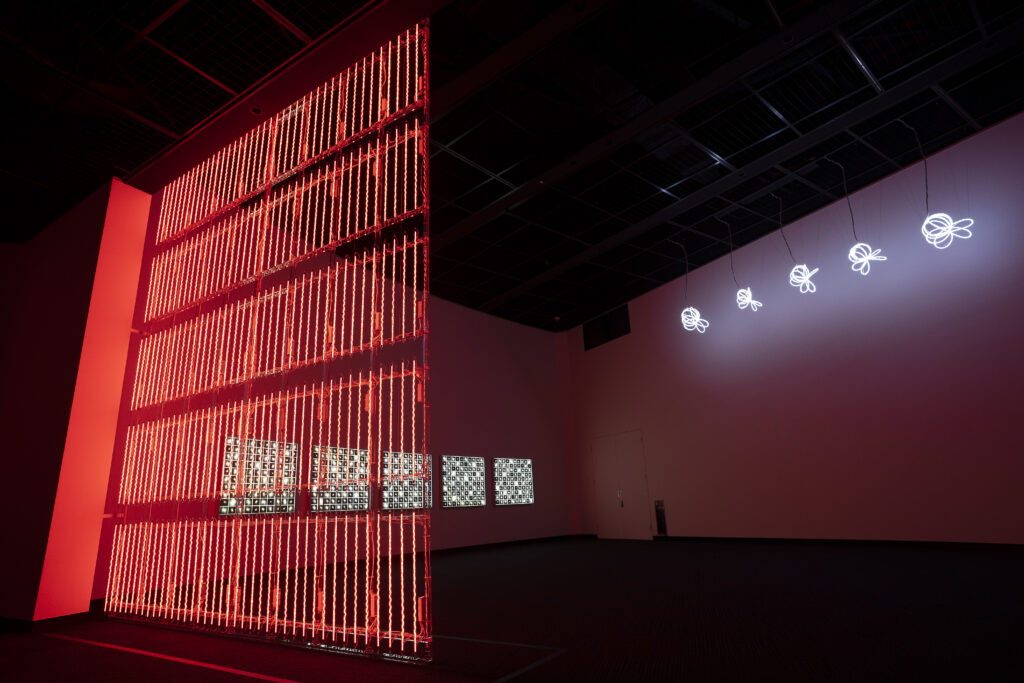
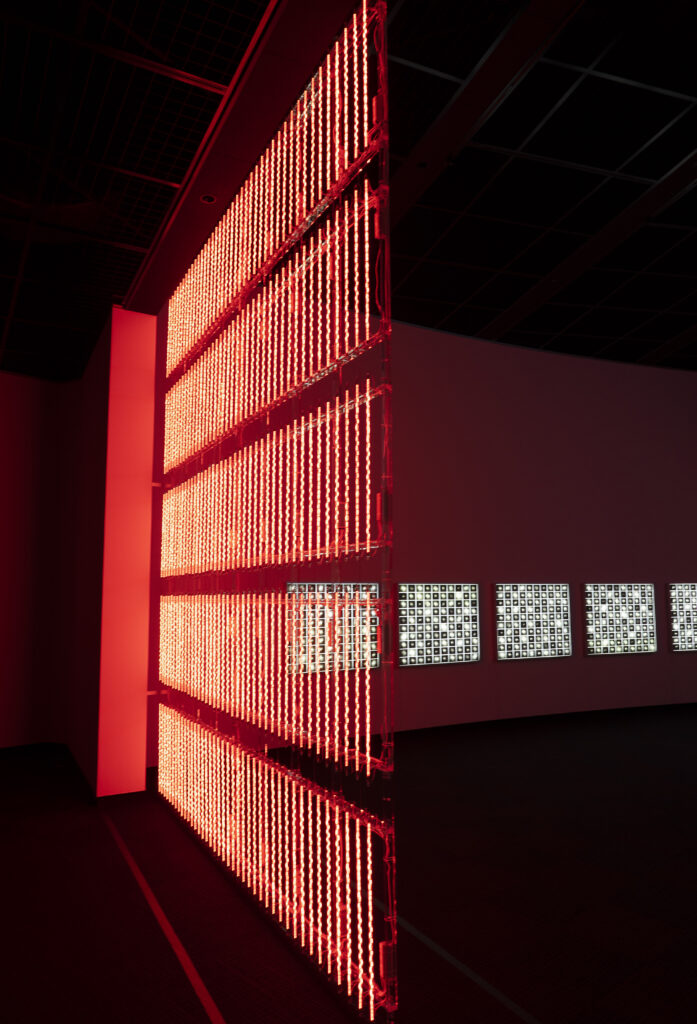
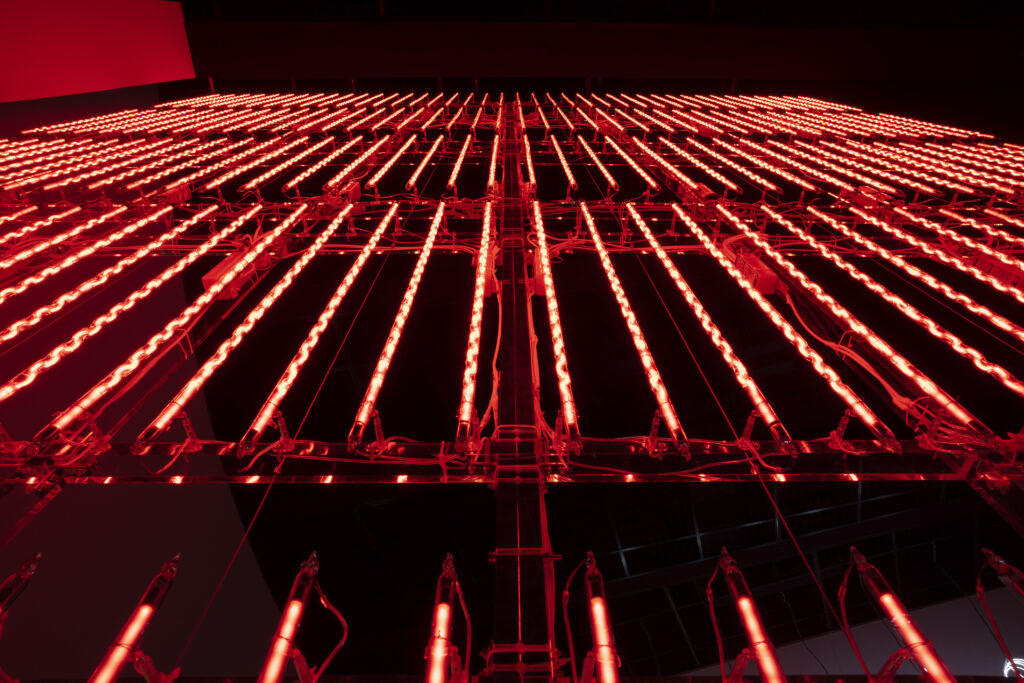
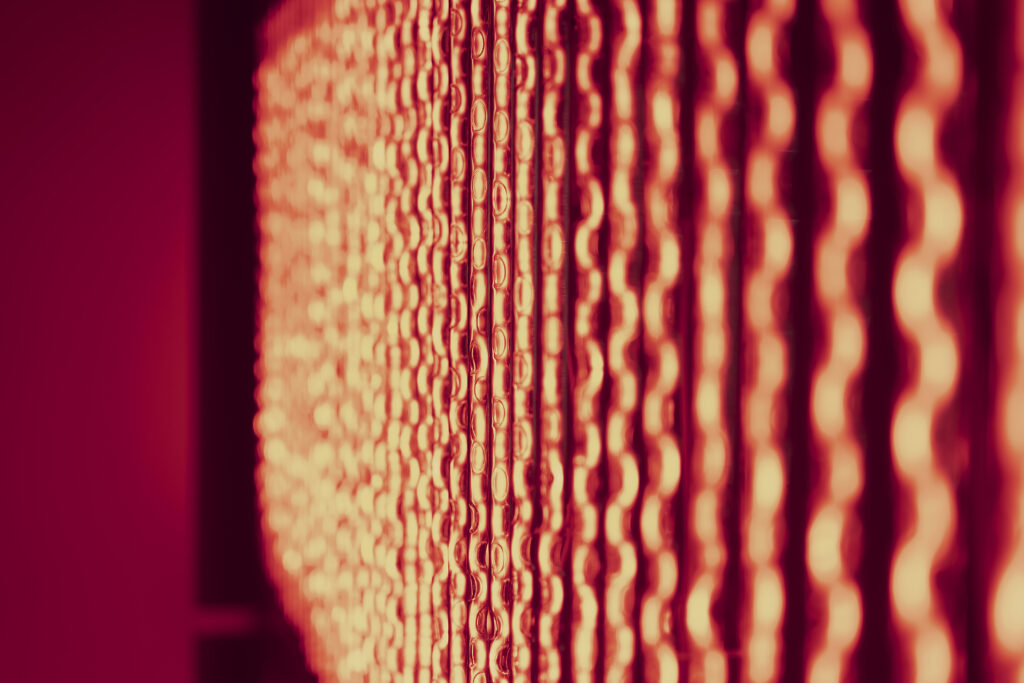
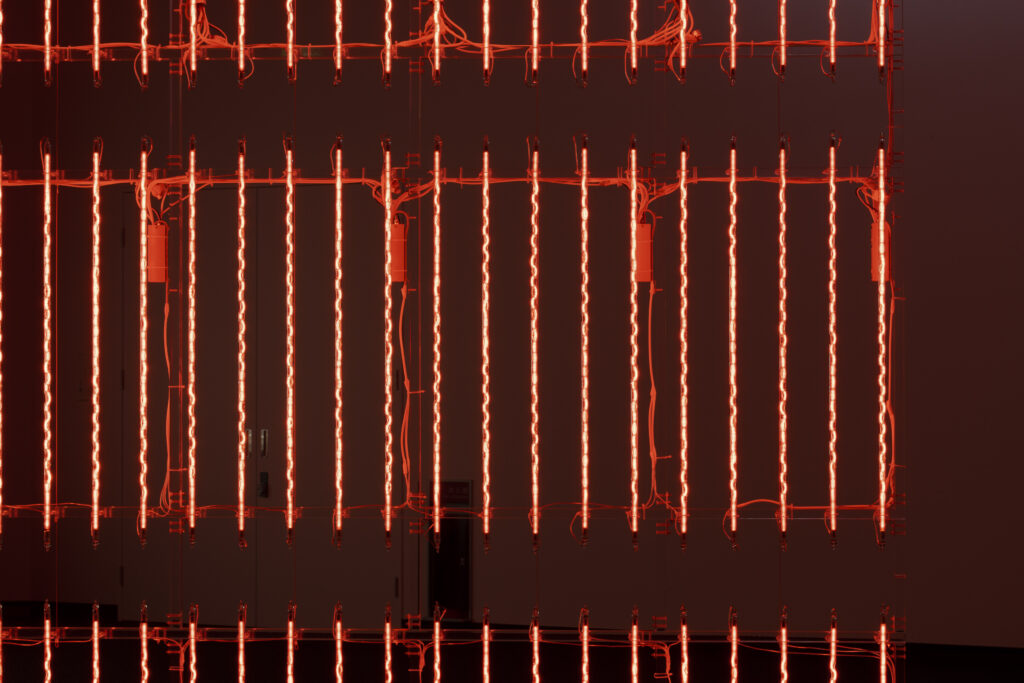
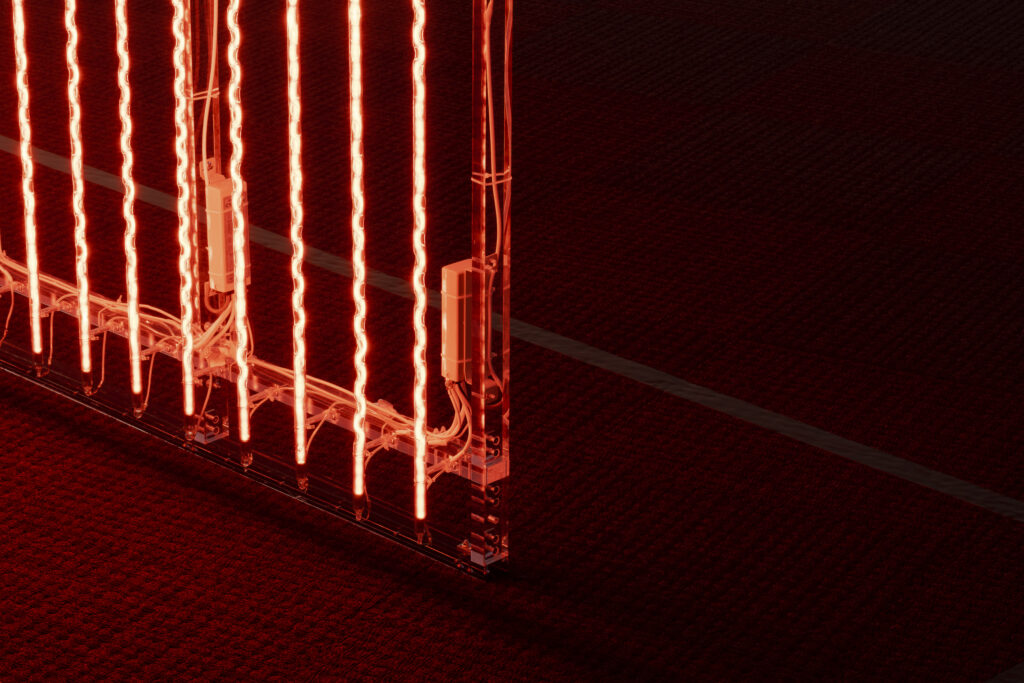
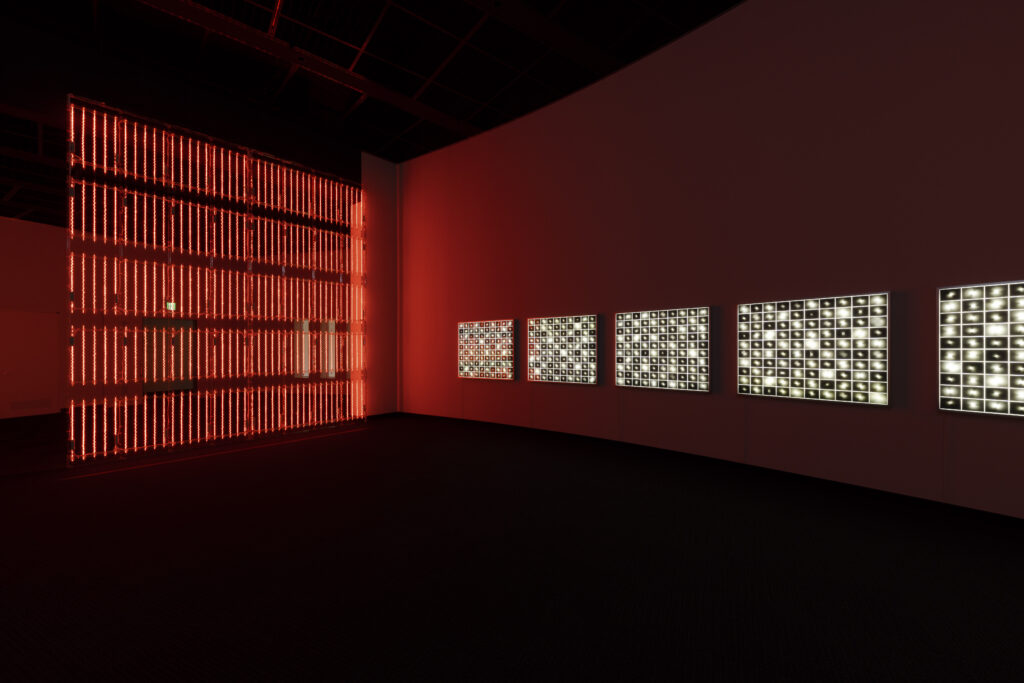
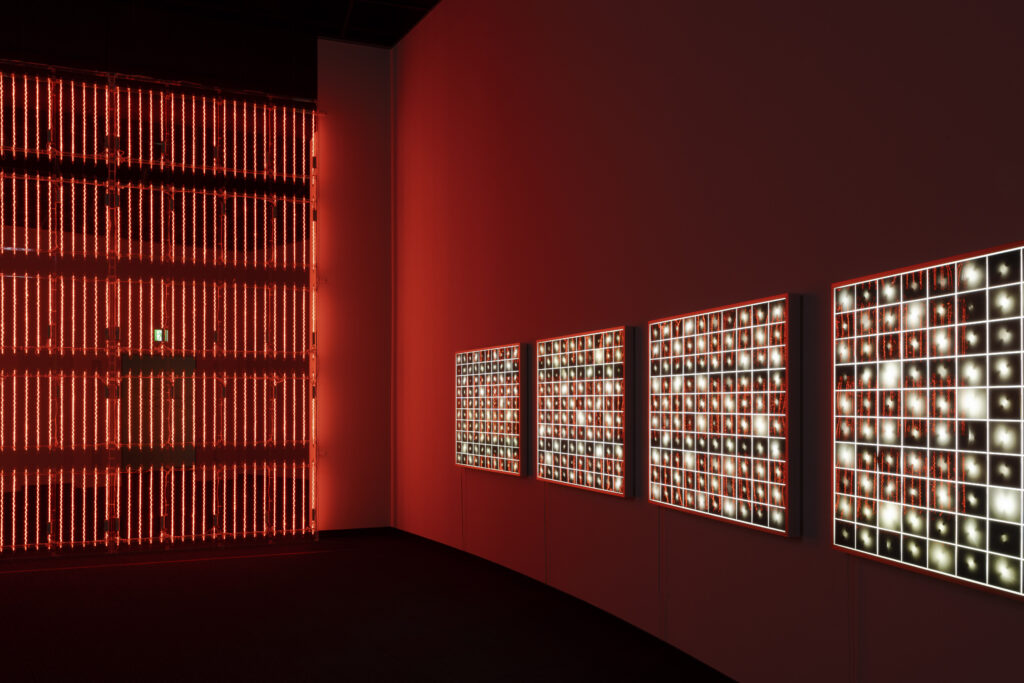
noise of the void | 2022
neon light, 1×10⁻⁵ Pa of vacuum, atmospheric pressure, acrylic
H4800 W4000 D100 (mm)
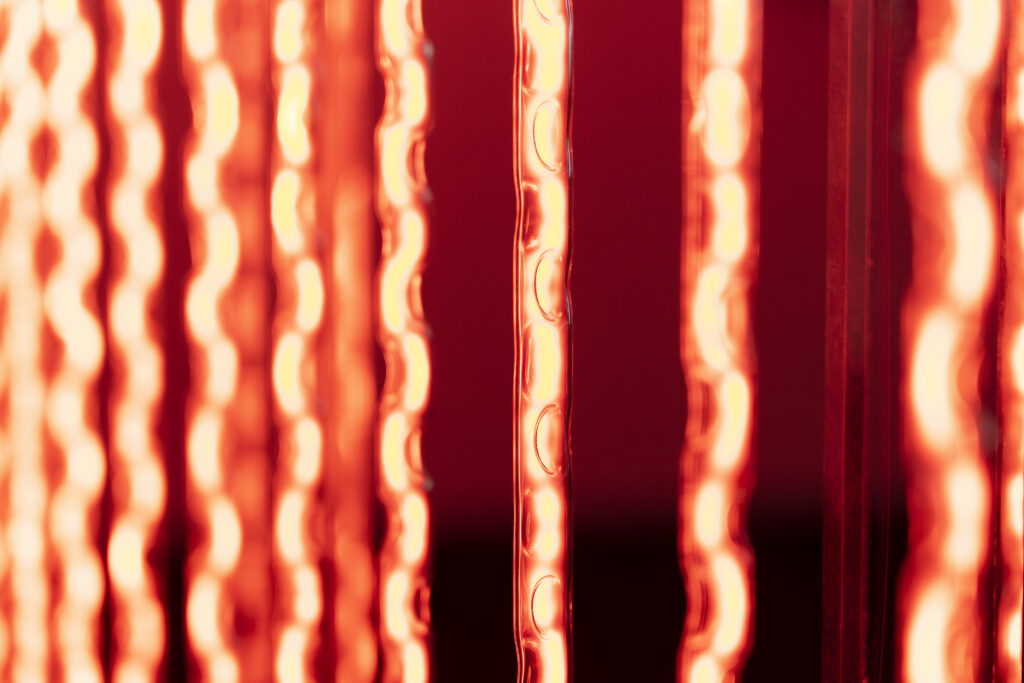
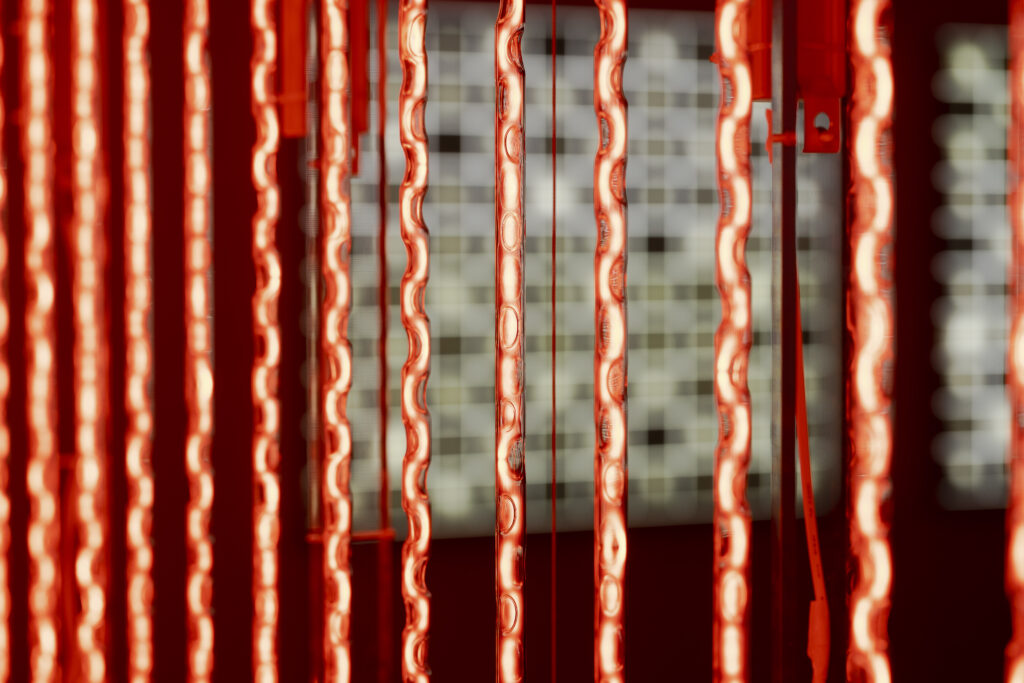
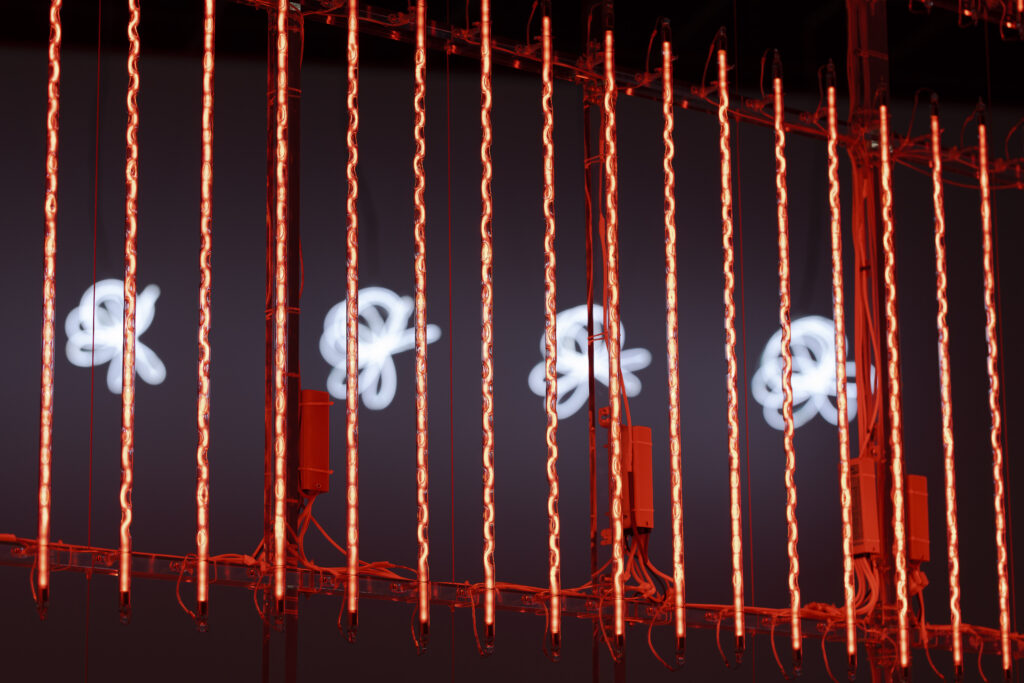
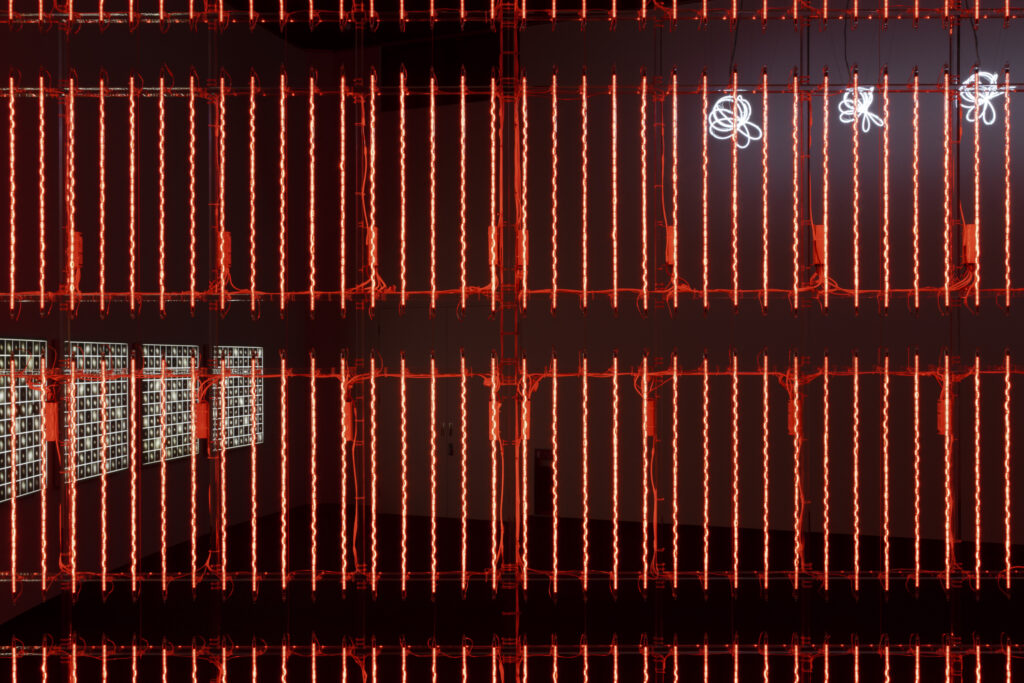
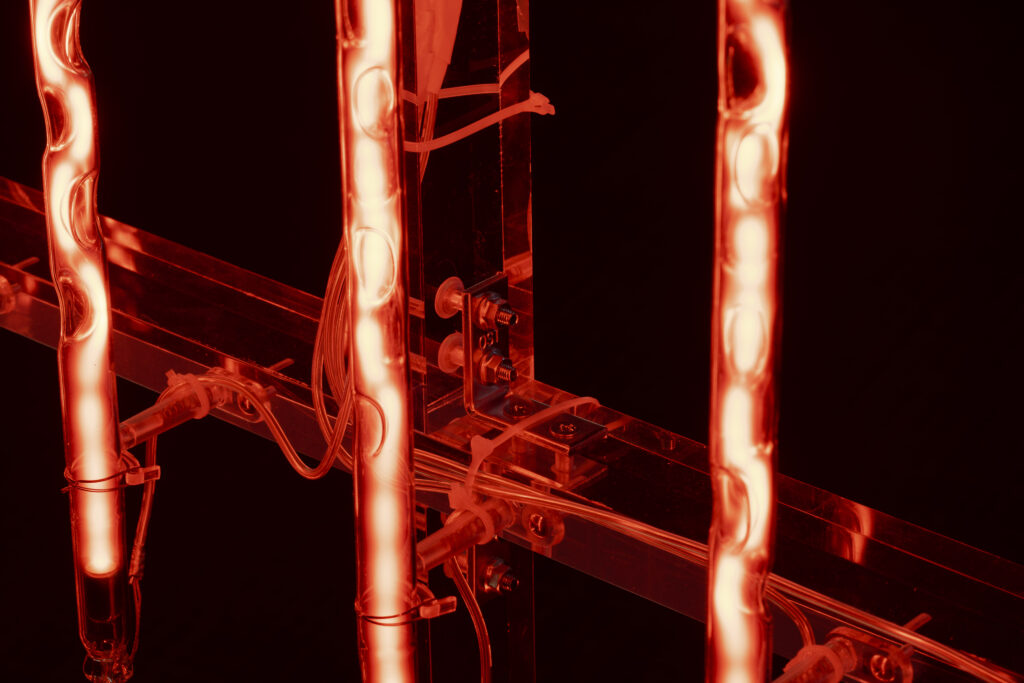
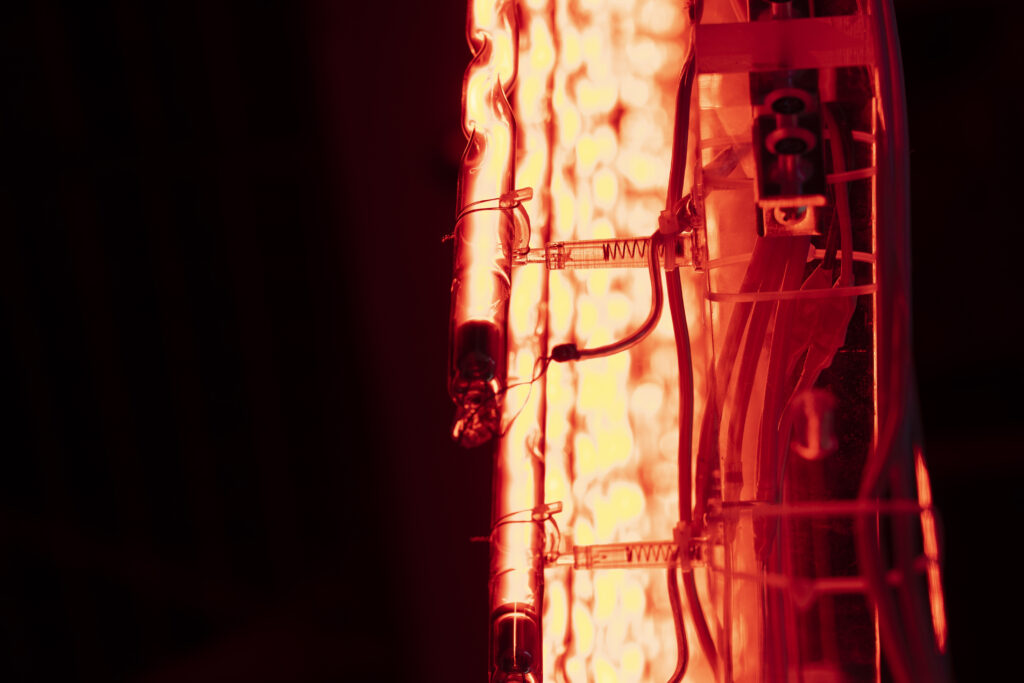
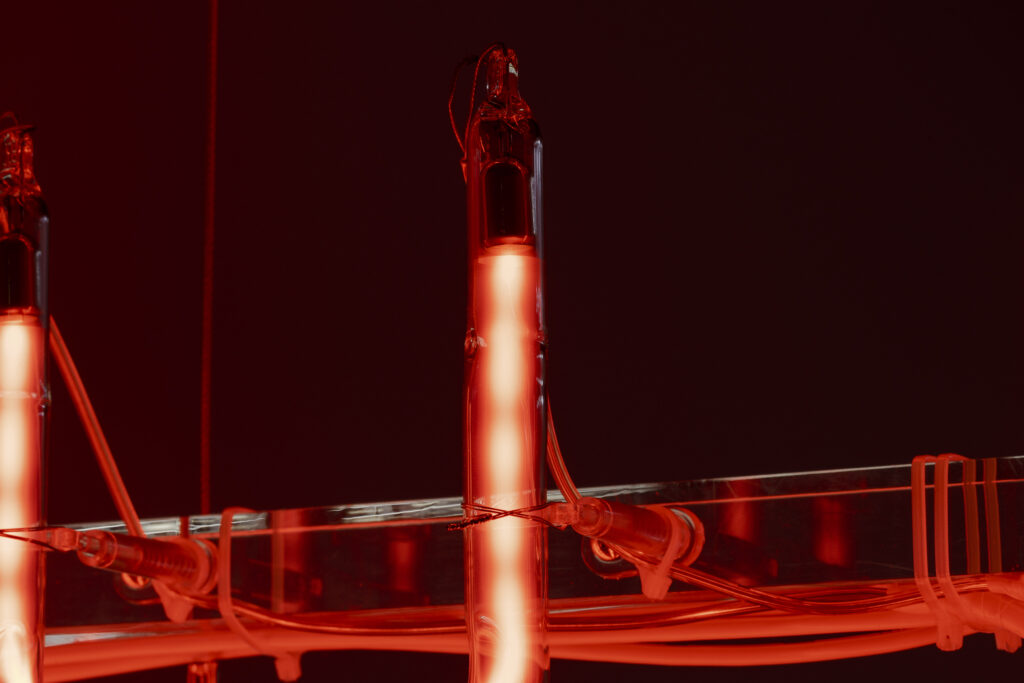
When a glass tube with a high vacuum inside is partially heated, the softened glass is pushed by the external atmospheric pressure (pulled by the internal vacuum) and the morphology of the glass tube changes. When neon gas is filled into the glass tube thus formed into a convex and concave shape by the force of the vacuum and high voltage is applied to the electrodes, irregular flickering and shimmering light is emitted. Electrons try to travel the shortest distance between the electrodes, but the path of the discharge is not regular as the space inside the glass tube narrows and widens. As a result, the resistance in the glass tube increases, resulting in an unstable discharge phenomenon with noise. This fluctuation of light reveals a part of the invisible noise that surrounds us and attempts to present something that exists between the self and others.